Music, sound, and frequency significantly influence brain function, emotional regulation, and productivity. By understanding how different frequencies affect brainwaves and neurotransmitter activity, we can use specific types of music to boost focus, creativity, and motivation. Instrumental and ambient music are particularly effective for maintaining concentration, while avoiding overly complex or emotionally heavy sounds can help prevent distractions. Crafting an optimal auditory environment by using consistent, calming sounds and minimizing disruptive stimuli is key to achieving peak productivity.
Music, sound, and frequency have a profound impact on how our brains function and how we behave. Historically, sound has been used to evoke emotions, help with healing, and improve overall well-being. Recent research has shown that specific types of music and sound frequencies can significantly enhance concentration, boost energy levels, and help maintain focus. This article explores how music, sound, and frequency are connected and how we can use them to improve productivity by managing our cognitive and emotional states effectively.
The human brain is highly responsive to music. Music can change our brainwave patterns, shift our emotions, and even influence our physical state. Researchers like Andrew Huberman, a neuroscientist at Stanford University, have shown that certain types of sounds can improve focus, mental performance, and emotional regulation. Understanding how music and sound affect our brains can help us choose which frequencies and rhythms are best for improving focus and optimizing energy. Music is not just an art form—it’s also a tool that can help us make our brain work more efficiently.
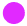
The auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the brain, is primarily responsible for processing sound. When we listen to music, this part of the brain becomes highly active, interpreting various components of the music, such as rhythm, pitch, and melody. Beyond the auditory cortex, other parts of the brain, including the limbic system (responsible for emotions) and the prefrontal cortex (involved in decision-making and attention), are also activated. This widespread activation explains why music can have such a strong effect on our emotions, cognitive performance, and overall mental state.
When sound waves enter our ears, they are converted into electrical signals by specialized cells called hair cells in the cochlea. These electrical signals then travel along the auditory nerve to different areas of the brain, where they are processed and interpreted.
The frequency of sound waves can directly influence the electrical activity in the brain, which we measure in brainwaves. Brainwaves are created by synchronized electrical pulses from neurons, and they come in different types—delta, theta, alpha, beta, and gamma—depending on their frequency. For example, gamma waves (30-100 Hz) are linked to increased cognitive functioning and intense focus, while alpha waves (8-14 Hz) promote relaxation while still keeping you alert.
Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz) are typically associated with deep sleep and restorative processes, while theta waves (4-8 Hz) are linked to creativity, daydreaming, and light meditation. Beta waves (14-30 Hz) are often present when we are actively thinking or engaged in problem-solving. Understanding how these different brainwave frequencies work can help us tailor our auditory environment to suit our needs, whether it's relaxation, creativity, or intense focus.
Certain sound frequencies can lead to brainwave entrainment, where external rhythms cause the brain's natural rhythms to synchronize with them, thereby altering our mental state. This means that sound can interact with the brain’s electrical signals, either enhancing or reducing certain activities to achieve desired outcomes, like better focus or relaxation.
Brainwave entrainment works through a process called the frequency-following response (FFR), where the brain naturally synchronizes its electrical activity with the frequency of an external auditory stimulus. For example, listening to a sound with a frequency in the alpha range can encourage the brain to produce more alpha waves, resulting in a relaxed but alert state. This interaction between sound frequencies and the brain’s electrical activity plays a significant role in mood, concentration, and energy levels. By using specific sound frequencies, we can change our mental state to improve productivity. For instance, binaural beats—which are created when two slightly different frequencies are played in each ear—can influence brainwaves and help induce states of relaxation, focus, or even deep meditation.
Gamma frequencies are particularly effective at improving concentration and problem-solving, making them ideal for tasks that require a lot of mental effort. Alpha frequencies, on the other hand, are good for relaxation without making you sleepy, allowing for a calm but focused state. Theta frequencies can be helpful for creative brainstorming, as they promote a more meditative and introspective state. Understanding which frequencies are suitable for specific mental tasks can make a significant difference in maintaining productivity.
Different types of music can affect the brain in different ways. Fast, energetic music can boost motivation and arousal, while calming, ambient music can help with relaxation and concentration. Studies suggest that instrumental music—such as classical, ambient, or lo-fi—is especially effective in helping people stay focused. Since instrumental music lacks lyrics, it doesn’t create additional cognitive load, making it easier to stay on task without distractions.
When we listen to music, the brain releases neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which can enhance mood and focus. Fast-tempo music with strong rhythms can increase the production of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter associated with alertness and arousal. This can be particularly useful when we need a burst of motivation to complete a challenging task. Conversely, slow-tempo music can increase the release of serotonin, promoting relaxation and emotional stability.
Many people who use music to stay productive report that instrumental playlists help them achieve a "flow" state. Flow is a mental state where a person becomes fully immersed in a task, often losing track of time. Music with repetitive rhythms and consistent beats is effective in achieving this state because it helps reduce distractions while maintaining mental engagement. The flow state is characterized by a balance between challenge and skill, and the right auditory background can facilitate this delicate balance by keeping the mind focused and minimizing intrusive thoughts.
However, not all music is good for productivity. Research shows that music with lyrics can be distracting during tasks that require language processing, like reading or writing, because the brain must split its attention between the lyrics and the main task. For this reason, instrumental music or other non-verbal sounds are often better for maintaining focus. Additionally, genres like heavy metal or music with erratic beats may disrupt the brain's natural rhythms, which can make it harder to concentrate. This is where the activity of neurotransmitters comes into play—using the right music can help balance brain chemicals, thereby improving focus and performance.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that allow neurons to communicate with each other, and they play a key role in regulating mood, focus, and behavior. Music and sound frequencies can affect the release of these neurotransmitters, which in turn influences cognitive function and productivity.
Dopamine is one of the main neurotransmitters involved in motivation and reward. Listening to music can stimulate the release of dopamine, which creates feelings of pleasure and helps maintain concentration. This dopamine boost helps keep us engaged in tasks, leading to improved focus. Conversely, music that creates negative emotions or chaotic auditory experiences may lower dopamine levels, resulting in decreased focus and motivation.
In addition to dopamine, other neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and endorphins also play important roles in how music affects cognitive performance. Serotonin is involved in mood regulation, and positive music can increase serotonin levels, leading to a more stable and focused state of mind. Norepinephrine is linked to alertness, and rhythmic, stimulating music can increase norepinephrine activity, enhancing attention and vigilance. Endorphins, which are natural chemicals that reduce pain and improve mood, are released in response to enjoyable music, promoting relaxation and well-being.
Research has shown that music can also reduce the levels of cortisol the hormone associated with stress. By lowering cortisol levels, music can help reduce anxiety and create a mental state that is more conducive to focus and productivity. This is particularly important during high-pressure situations, where managing stress is crucial for maintaining performance.
Understanding how these neurotransmitters interact with auditory stimuli is crucial for optimizing focus and productivity. Relaxing sounds that maintain dopamine and serotonin levels can support sustained focus, while sounds that lead to fatigue or boredom should be avoided during challenging tasks. By customizing our auditory environment to influence neurotransmitter activity, we can enhance focus, motivation, and mental clarity.
Mood and energy levels are closely linked to productivity. Sounds and music can directly affect both emotional states and our ability to focus. Positive, upbeat sounds can lift our mood, making work feel less like a chore and more enjoyable, which in turn can improve motivation and resilience.
The limbic system, which is responsible for processing emotions, is highly responsive to auditory stimuli. When we listen to music that resonates with us emotionally, the limbic system becomes active, leading to changes in mood and emotional state. For example, music with a positive, uplifting tone can stimulate the release of dopamine and endorphins, creating a sense of pleasure and motivation. On the other hand, exposure to stressful or negative sounds can increase the production of cortisol, leading to heightened anxiety and reduced focus.
By carefully selecting the sounds we listen to, we can create an emotional environment that supports higher productivity and well-being. Recognizing the connection between auditory stimuli and mood is key to improving productivity. Crafting a personalized auditory environment that aligns with our emotional and cognitive needs can greatly enhance our ability to perform tasks effectively. For instance, listening to nature sounds or calming instrumental music during breaks can help reset our mood and prepare us for the next task with renewed focus.
What to Avoid: Sounds That Undermine Productivity
To maximize productivity, it is important to be mindful of the types of music and sounds we use while working. Not all sounds are beneficial, and certain types can have a negative impact on our focus, mood, and overall efficiency. Here are some key points to consider:
Recommendations for a Productive Sound Environment
To create an optimal auditory environment, consider the following recommendations:
By carefully selecting the types of sounds we expose ourselves to while working, we can create an environment that not only supports focus but also enhances our overall well-being and productivity. The right auditory environment can make a significant difference in how effectively we complete tasks and manage our mental energy throughout the day. This understanding of how sound influences our productivity sets the stage for creating personalized strategies to achieve peak performance.
Conclusion: Crafting Your Optimal Sound Environment
In conclusion, the sounds we choose to surround ourselves with play a powerful role in shaping our mental state, mood, and productivity. By using instrumental or ambient music, maintaining consistent volume levels, and experimenting with nature sounds, we can create an environment that is conducive to focused and efficient work. Avoiding overly stimulating or distracting genres can further enhance our ability to stay on task and maintain clarity of thought.
At Personal Productivity Hub, we provide curated playlists tailored for different types of work—whether you need deep focus, relaxation, or an energy boost. By being intentional about your sound environment, you can significantly enhance your productivity and create a more enjoyable work experience.
Remember, achieving peak productivity is not just about having the right tools or techniques—it is also about fostering an environment that aligns with your cognitive and emotional needs. Sound is a crucial part of that environment, and when used thoughtfully, it can be a game-changer in how you work and live.